Capacity utilization: Definition, Measurement and Utilization [2024]

Capacity utilization refers to the extent to which a firm or economy uses its installed productive capacity to meet the demands of its products or services. It is a critical concept in economics, business management, and policymaking, as it directly influences production efficiency, profitability, and overall economic performance.
Definition and Measurement of Capacity Utilization
1. Definition
Capacity utilization refers to the ratio of actual output produced by a firm or economy to its maximum potential output if all resources were fully utilized. It is often expressed as a percentage, where 100% indicates full capacity utilization.
2. Measurement
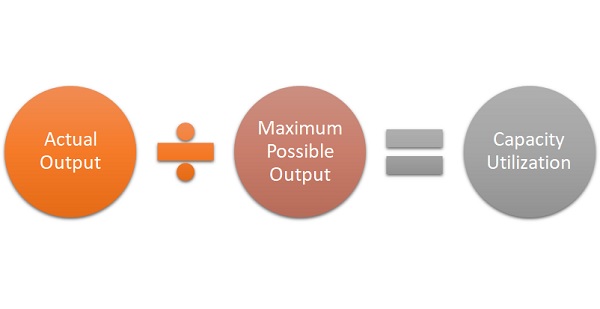
Capacity utilization can be measured at different levels:
- Firm Level: Firms measure capacity utilization by comparing actual output with their maximum production capacity.
- Industry Level: Industries gauge capacity utilization by aggregating data from individual firms within the sector.
- Macro Level: Economists assess capacity utilization at the national or global level, considering various industries’ aggregate output relative to their potential capacity.
Factors Influencing Capacity Utilization
1. Demand Dynamics
- Market Demand: Fluctuations in consumer demand directly impact capacity utilization. High demand may lead to full capacity utilization, while low demand can result in idle capacity.
- Seasonality: Industries such as tourism experience seasonal fluctuations, affecting capacity utilization throughout the year.
2. Supply-Side Factors
- Technological Change: Advances in technology can enhance productive capacity, leading to higher utilization rates.
- Capital Investment: Investment in new machinery or infrastructure expands capacity, influencing utilization levels.
- Labor Availability: Skilled labor shortages or surpluses can influence production levels and capacity utilization.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Interruptions in the supply chain, such as raw material shortages or logistics delays, can hinder production and reduce capacity utilization.
3. Economic Environment
- Interest Rates: Monetary policy and interest rates influence firms’ investment decisions in expanding capacity.
- Government Policies: Regulatory policies, taxation, and subsidies can impact firms’ incentives to invest in capacity expansion.
- Business Confidence: Economic uncertainty can deter firms from making long-term capacity expansion decisions, impacting utilization rates.
Importance of Capacity Utilization
1. Production Efficiency
- Optimal capacity utilization enhances production efficiency, minimizing per-unit production costs and maximizing profitability.
- It enables firms to achieve economies of scale, spreading fixed costs over a larger output quantity.
2. Resource Allocation
- Efficient capacity utilization ensures optimal allocation of resources, preventing overinvestment or underutilization of capital and labor.
- It contributes to the efficient allocation of scarce resources in the economy, fostering overall economic growth.
3. Pricing and Competition
- Capacity utilization influences pricing dynamics in markets. High utilization rates may lead to higher prices due to supply constraints, while low utilization rates can result in price competition.
- It influences firms’ competitiveness by determining their ability to meet market demand effectively.
4. Economic Stability
- Capacity utilization is closely linked to overall economic stability. High utilization rates indicate strong economic activity, while low rates may signal economic downturns or recessions.
- It serves as an important indicator for policymakers in assessing the health of the economy and formulating appropriate fiscal and monetary policies.
Capacity Utilization in Different Sectors
1. Manufacturing
- Capacity utilization is a critical concern in manufacturing industries due to high fixed costs associated with production facilities.
- Industries such as automotive and electronics closely monitor capacity utilization to optimize production schedules and meet fluctuating demand.
2. Services
- Service industries, including healthcare, hospitality, and transportation, also grapple with capacity utilization challenges.
- Hospitals strive to maintain optimal bed occupancy rates, while airlines manage seat capacity to balance demand and supply.
3. Infrastructure
- Infrastructure sectors, such as energy and telecommunications, require substantial investment in capacity expansion to accommodate growing demand.
- Governments play a significant role in planning and funding infrastructure projects to ensure adequate capacity utilization.
Strategies to Optimize Capacity Utilization
1. Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting helps firms anticipate future demand patterns and adjust capacity, accordingly, minimizing underutilization or over utilization risks.
2. Flexible Production Systems: Adopting flexible production systems enables firms to adjust output levels in response to demand fluctuations, enhancing capacity utilization efficiency.
3. Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management practices reduce the risk of overstocking or stock outs, ensuring optimal utilization of production capacity.
4. Technology Investment: Investing in advanced technologies enhances productivity and expands capacity, enabling firms to achieve higher utilization rates.
5. Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with suppliers and distributors facilitates smoother supply chain operations, reducing the likelihood of disruptions and improving capacity utilization.
Conclusion
Capacity utilization is a multifaceted concept that influences production efficiency, resource allocation, pricing dynamics, and overall economic stability. Understanding the factors influencing capacity utilization and implementing strategies to optimize it are crucial for firms and policymakers alike.
By maintaining optimal capacity utilization levels, organizations can enhance competitiveness, profitability, and economic growth in the long run.
Read also:
- Understanding of NNP (Net Nation Product)
- 15 FAQ on Personal Finance
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- 15 FAQ on 80-20 Rule (Pareto Principle)
- Depreciation- Meaning, Definition, Types and Calculation
- Fiscal Deficit- Definition, Calculation and Significance
- Balance of Payments (BoP): Explained
- Balance of Trade: Definition, Measurement and Significance
- Allocative efficiency: Definition, Meaning and Significance
- Automatic stabilizers: Definition, Mechanism and Significance


![What is Miami Heat? History and Importance [2024]](https://anyfaq.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/What-is-Miami-Heat-768x432.jpg)



